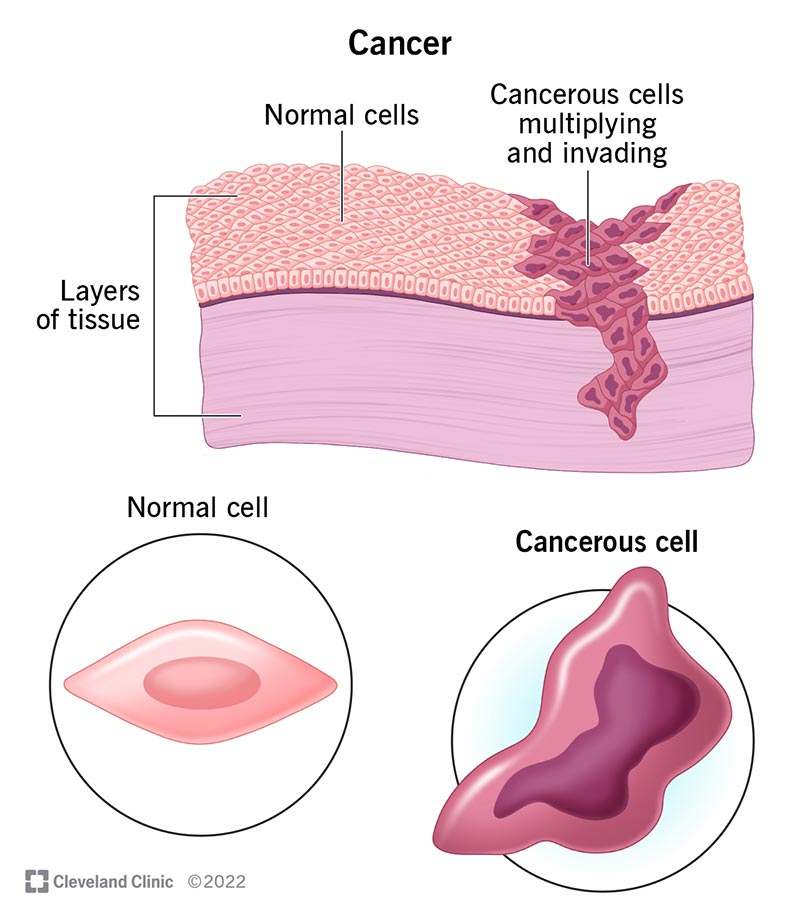
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells in the body. These cells can invade and destroy surrounding tissues and organs. Understanding the basic concepts of cancer is essential in raising awareness and supporting efforts towards prevention and treatment.
Causes of Cancer
While the exact causes of cancer are not always clear, several factors can contribute to the development of the disease, including:
- Genetic mutations
- Exposure to carcinogens
- Unhealthy lifestyle choices
- Breast cancer: Affects the breast tissue in both men and women.
- Lung cancer: Develops in the lungs and can be caused by smoking or environmental factors.
- Colon cancer: Occurs in the colon or rectum and is often related to diet and genetics.
- Surgery: Removes cancerous tumors from the body.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
- Radiation therapy: Targets and destroys cancer cells using high-energy rays.
Types of Cancer
There are various types of cancer that can affect different parts of the body. Some common types include:
Treatment Options
Treating cancer often involves a combination of therapies tailored to the type and stage of the disease. Common treatment options include:
It is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing support when dealing with cancer.
What are the types of Cancer?
There are numerous types of cancer that affect different parts of the body and have varying characteristics. Understanding the different types of cancer is important for early detection and appropriate treatment. Here are some common types of cancer:
Solid Tumor Cancers
Solid tumors are masses of tissue that develop when cells grow and divide uncontrollably. These can be cancerous or benign. Some common types of solid tumor cancers include:
- Breast Cancer: Affects the breast tissue and can occur in both men and women.
- Lung Cancer: Arises in the lungs and is often linked to smoking or exposure to toxins.
- Prostate Cancer: Develops in the prostate gland of men and is a common cancer in older men.
- Leukemia: Cancer of the blood cells, affecting the bone marrow and bloodstream.
- Lymphoma: Cancer of the lymphatic system, which includes Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
- Myeloma: Cancer that develops in the plasma cells, a type of white blood cell.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: The most common type of skin cancer that often appears on sun-exposed areas.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Another common skin cancer that can also occur on sun-exposed skin.
- Melanoma: A more aggressive form of skin cancer that can spread to other parts of the body.
Hematologic Cancers
Hematologic cancers affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. These types of cancers include leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma:
Skin Cancers
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer, usually caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Some types of skin cancer include:
These are just a few examples of the types of cancer that exist. Each type of cancer requires specific diagnosis and treatment strategies, so it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals if you have any concerns about your health.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/more-cancer-types-4158486_final1-32133bd225444ae0a3b6be96d62de7bf.jpg)
Reasons for Cancer
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of cancer. Understanding these reasons can help in prevention and early detection.
1. Genetic Factors
- Family History: Inherited genetic mutations can increase the risk of various cancers.
- Genetic Mutations: Changes in genes can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer development.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and tobacco products are linked to several types of cancer.
- Poor Diet: Lack of fresh fruits and vegetables, and high consumption of processed foods can contribute to cancer risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is associated with an increased risk of cancer.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity can contribute to obesity and increase cancer risk.
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Contact with substances like asbestos, radon, and industrial chemicals can raise cancer risk.
- UV Radiation: Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or tanning beds can lead to skin cancer.
- HPV and Hepatitis Viruses: Infections with certain viruses can increase the likelihood of developing specific types of cancer.
- H. pylori Bacteria: Infection with this bacteria is linked to stomach cancer.
2. Lifestyle Choices
3. Environmental Factors
4. Infectious Agents
By being aware of these reasons for cancer, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and prioritize their health.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cancer-causes-513773_FINAL-ed7f995b3eca46eca8064643b15ce581.jpg)
What is a remedy of Cancer?
Cancer remedies are approaches, treatments, or therapies aimed at managing cancer, reducing its progression, or attempting to eliminate cancer cells from the body. These remedies can vary depending on the type of cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the patient.
Common Types of Cancer Remedies:
- 1. Surgery: Surgical procedures are often used to remove cancerous tumors or tissues from the body.
- 2. Chemotherapy: The use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
- 3. Radiation Therapy: The use of high-energy rays or particles to target and destroy cancer cells.
- 4. Immunotherapy: Treatment that boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
- 5. Targeted Therapy: Treatment that targets specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- 1. Palliative Care: Focuses on improving the quality of life for individuals with cancer through symptom management and support.
- 2. Clinical Trials: Participation in research studies to test new cancer treatments.
- 3. Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM): Practices such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, or mind-body therapies that may be used alongside conventional cancer treatments.
Other Considerations for Cancer Remedies: